Please cite:
Serizay J, Matthey-Doret C, Bignaud A, Baudry L, Koszul R (2024). “Orchestrating chromosome conformation capture analysis with Bioconductor.” Nature Communications, 15, 1-9. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-44761-x.
The HiCool R/Bioconductor package provides an end-to-end interface to process and normalize Hi-C paired-end fastq reads into .(m)cool files.
- The heavy lifting (fastq mapping, pairs parsing and pairs filtering) is performed by the underlying lightweight
hicstuffpython library (https://github.com/koszullab/hicstuff). - Pairs filering is done using the approach described in Cournac et al., 2012 and implemented in
hicstuff. -
Cooler(https://github.com/open2c/cooler) library is used to parse pairs into a multi-resolution, balanced.mcoolfile..(m)coolis a compact, indexed HDF5 file format specifically tailored for efficiently storing HiC-based data. The.(m)coolfile format was developed by Abdennur and Mirny and published in 2019. - Internally, all these external dependencies are automatically installed and managed in R by a
basiliskenvironment.
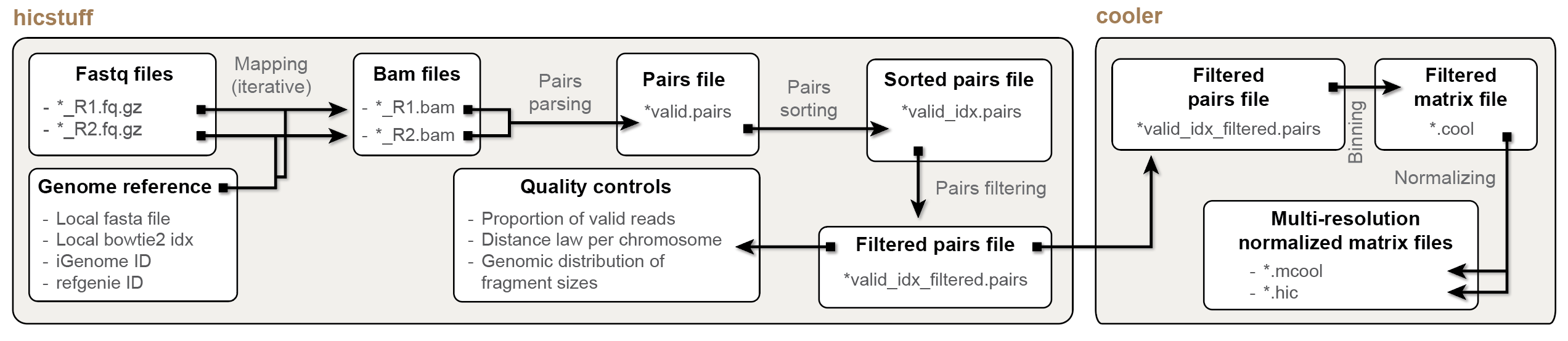
Processing .fastq paired-end files into a .mcool Hi-C contact matrix
The main processing function offered in this package is HiCool(). One simply needs to specify:
- The path to each fastq file;
- The genome reference, as a
.fastasequence, a pre-computedbowtie2index or a supported ID (hg38,mm10,dm6,R64-1-1,WBcel235,GRCz10,Galgal4); - The restriction enzyme(s) used for Hi-C.
library(HiCool)
x <- HiCool(
r1 = '<PATH-TO-R1.fq.gz>',
r2 = '<PATH-TO-R2.fq.gz>',
restriction = 'DpnII,HinfI',
genome = 'R64-1-1'
)## HiCool :: Recovering bowtie2 genome index from AWS iGenomes...
## HiCool :: Initiating processing of fastq files [tmp folder: /tmp/RtmpARIRQo/DZ28I8]...
## HiCool :: Mapping fastq files...
## HiCool :: Best-suited minimum resolution automatically inferred: 1000
## HiCool :: Remove unwanted chromosomes...
## HiCool :: Generating multi-resolution .mcool file...
## HiCool :: Balancing .mcool file...
## HiCool :: Tidying up everything for you...
## HiCool :: .fastq to .mcool processing done!
## HiCool :: Check /home/rsg/repos/HiCool/HiCool folder to find the generated files
## HiCool :: Generating HiCool report. This might take a while.
## HiCool :: Report generated and available @ sample^mapped-R64-1-1^DZ28I8.html
## HiCool :: All processing successfully achieved. Congrats!
xOutput files
## HiCool/
## |-- sample^mapped-R64-1-1^55IONQ.html
## |-- logs
## | |-- sample^mapped-R64-1-1^55IONQ.log
## |-- matrices
## | |-- sample^mapped-R64-1-1^55IONQ.mcool
## |-- pairs
## | |-- sample^mapped-R64-1-1^55IONQ.pairs
## `-- plots
## |-- sample^mapped-R64-1-1^55IONQ_event_distance.pdf
## |-- sample^mapped-R64-1-1^55IONQ_event_distribution.pdfReporting
On top of processing fastq reads, HiCool provides convenient reports for single/multiple sample(s).
x <- importHiCoolFolder(output = 'HiCool/', hash = '55IONQ')
HiCReport(x)Installation
As an R/Bioconductor package, HiCool should be very easy to install. The only dependency is R (>= 4.2). In R, one can run:
if (!require("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("HiCool")The first time a HiCool() function is executed, a basilisk environment will be automatically set up. In this environment, few dependencies will be installed:
- python (pinned 3.9.1)
- numpy (pinned 1.23.4)
- bowtie2 (pinned 2.4.5)
- samtools (pinned 1.7)
- hicstuff (pinned 3.1.5)
- cooler (pinned 0.8.11)
HiCExperiment ecosystem
HiCool is integrated within the HiCExperiment ecosystem in Bioconductor. Read more about the HiCExperiment class and handling Hi-C data in R here.
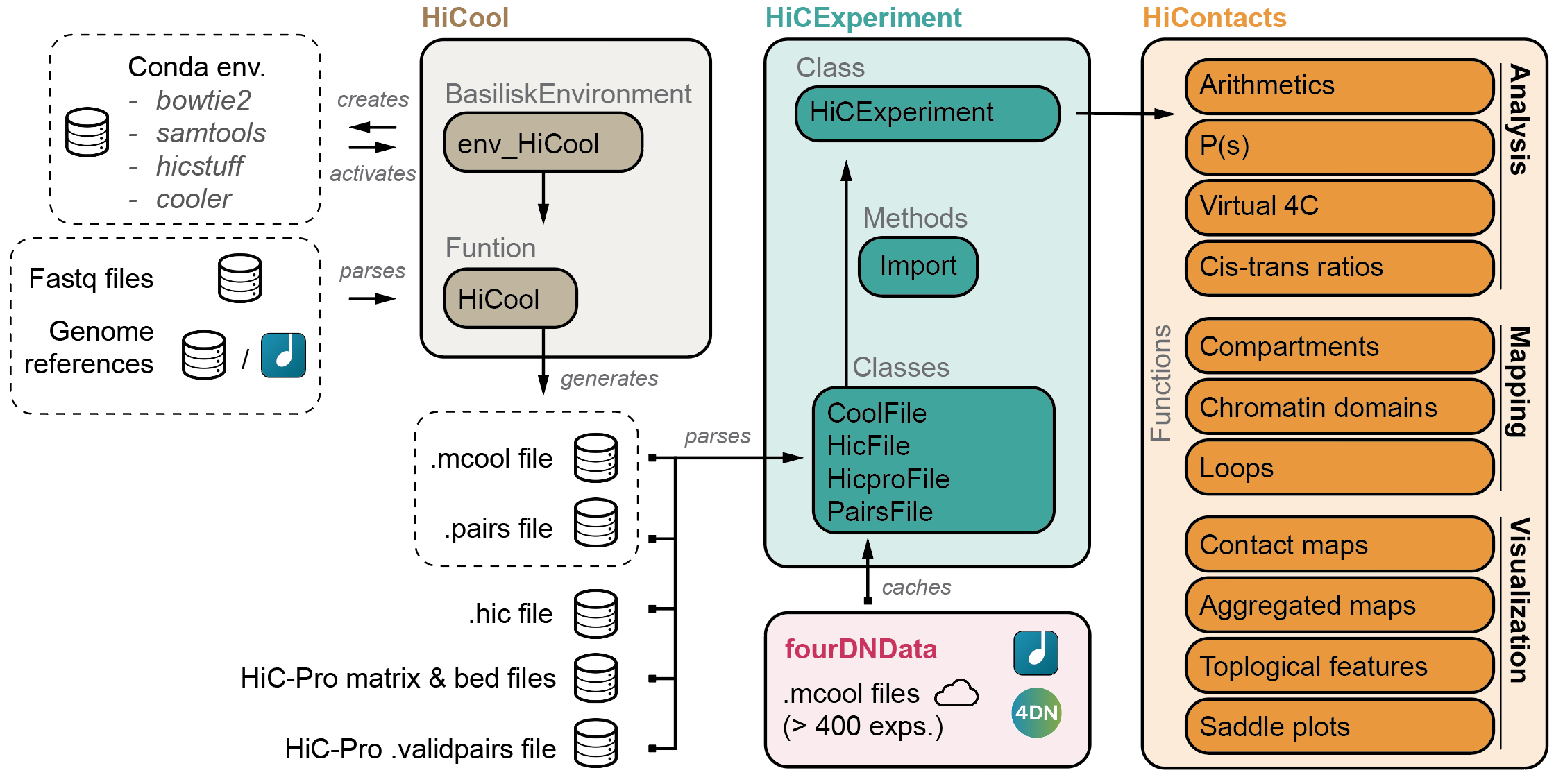
- HiCExperiment: Parsing Hi-C files in R
- HiCool: End-to-end integrated workflow to process fastq files into .cool and .pairs files
- HiContacts: Investigating Hi-C results in R
- HiContactsData: Data companion package
- fourDNData: Gateway package to 4DN-hosted Hi-C experiments


